Hanspers K, Kutmon M, Coort SL, Digles D, Dupuis LJ, Ehrhart F, et al. (2021) Ten simple rules for creating reusable pathway models for computational analysis and visualization. PLoS Comput Biol 17(8): e1009226.
DOI
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pcbi.1009226
Introduction
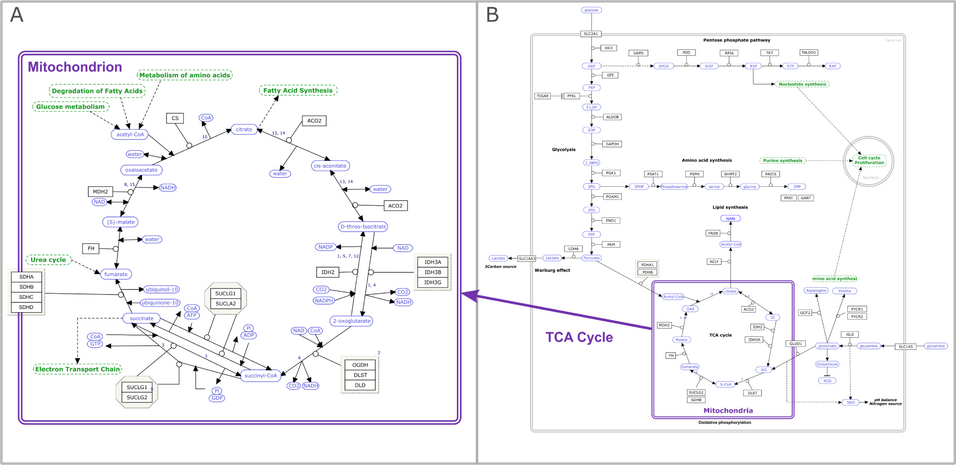
Pathway models are an effective way to capture and share our current understanding of biological processes. A pathway model is defined here as a set of interactions among biological entities (e.g., proteins and metabolites) relevant to a particular context, curated and organized to illustrate a particular process. Properly modeled pathways can be used in the analysis and visualization of diverse types of omics and other biomedical data [1,2]. The modeling process involves taking our knowledge about biological pathways—however messy and incomplete—and encoding it in standardized data formats that can be shared, reused, and synthesized with other knowledge in accordance with the Findable, Accessible, Interoperable, and Reusable (FAIR) principles [3]. The rules presented here serve as an introduction and guide to the pathway modeling process, leveraging freely available tools and resources. [...]
Funding
This work was funded by the European Union’s Horizon 2020 Research and Innovation Programme [OpenRiskNet: 731075 to MM, CTE; EJP-RD: 825575 to FE, WS, CTE; FNS-Cloud: 863059 to SLC, CTE; EU-ToxRisk: 681002 to MM, CTE; NanoCommons: 731032 to ELW, LAW], ZonMw [10430012010015 to MK, SLC, LJD, FE, FH, NP, ELW, CTE] and the National Institute of General Medical Sciences [R01 GM100039 to KH, ARP; R01 GM089820 to AW]. The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
Copyright
© 2021 Hanspers et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.