Abstract
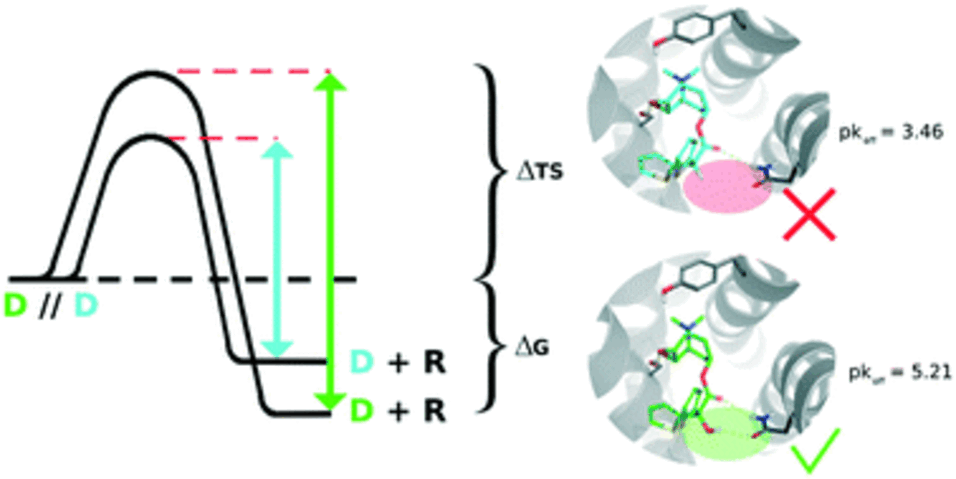
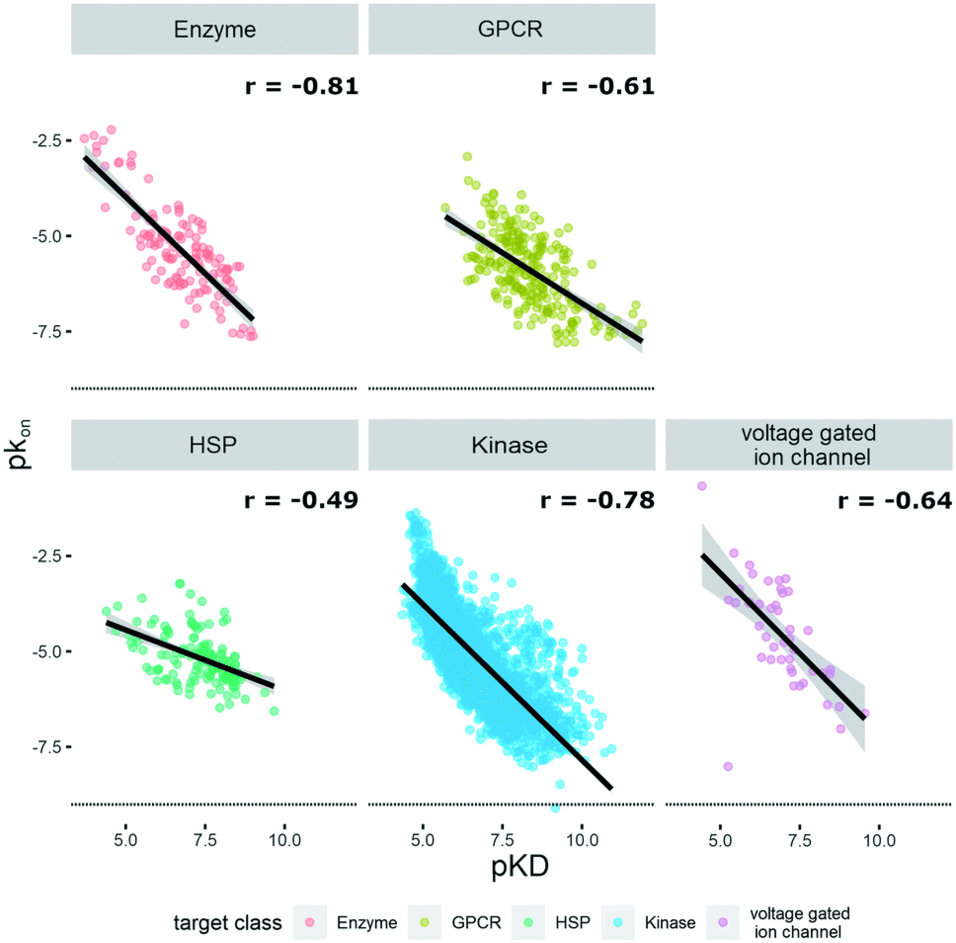
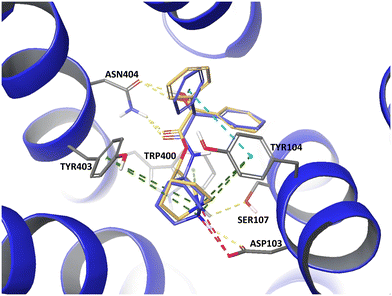
The lifetime of a binary drug–target complex is increasingly acknowledged as an important parameter for drug efficacy and safety. With a better understanding of binding kinetics and better knowledge about kinetic parameter optimization, intentionally induced prolongation of the drug–target residence time through structural changes of the ligand could become feasible. In this study we assembled datasets from 21 publications and the K4DD (Kinetic for Drug Discovery) database to conduct large scale data analysis. This resulted in 3812 small molecules annotated to 78 different targets from five protein classes (GPCRs: 273, kinases: 3238, other enzymes: 240, HSPs: 160, ion channels: 45). Performing matched molecular pair (MMP) analysis to further investigate the structure–kinetic relationship (SKR) in this data collection allowed us to identify a fundamental contribution of a ligand's polarity to its association rate, and in selected cases, also to its dissociation rate. However, we furthermore observed that the destabilization of the transition state introduced by increased polarity is often accompanied by simultaneous destabilization of the ground state resulting in an unaffected or even worsened residence time. Supported by a set of case studies, we provide concepts on how to alter ligands in ways to trigger on-rates, off-rates, or both.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the EU/EFPIA Innovative Medicines Initiative (IMI) Joint Undertaking, K4DD (grant no. 1115366). This paper reflects only the authors' views and neither the IMI nor the European Commission is liable for any use that may be made of the information contained herein. Furthermore, we want to thank Bernhard Knasmüller for support on the methodologies for the database structure.
Copyright
D. A. Schuetz, L. Richter, R. Martini and G. F. Ecker, RSC Med. Chem., 2020, Advance Article , DOI: 10.1039/D0MD00178C
This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported Licence. Material from this article can be used in other publications provided that the correct acknowledgement is given with the reproduced material.