Anna Schrempf, Sara Bernardo, Emili A. Arasa Verge, Miguel A. Ramirez Otero, Jordan Wilson, Dominik Kirchhofer, Gerald Timelthaler, Anna M. Ambros, Atilla Kaya, Marcus Wieder, Gerhard F. Ecker, Georg E. Winter, Vincenzo Costanzo, Joanna I. Loizou, POLθ processes ssDNA gaps and promotes replication fork progression in BRCA1-deficient cells, Cell Reports, Volume 41, Issue 9, 2022.
DOI
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2022.111716
Abstract
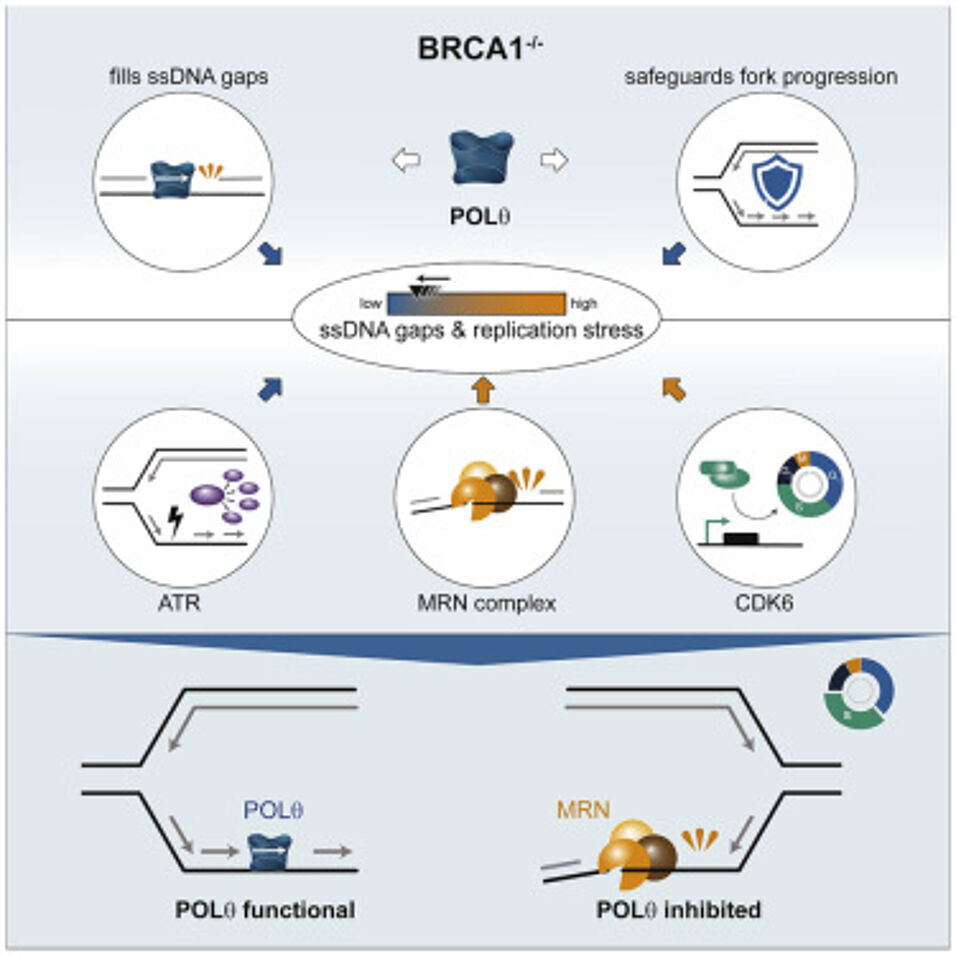
Polymerase theta (POLθ) is an error-prone DNA polymerase whose loss is synthetically lethal in cancer cells bearing breast cancer susceptibility proteins 1 and 2 (BRCA1/2) mutations. To investigate the basis of this genetic interaction, we utilized a small-molecule inhibitor targeting the POLθ polymerase domain. We found that POLθ processes single-stranded DNA (ssDNA) gaps that emerge in the absence of BRCA1, thus promoting unperturbed replication fork progression and survival of BRCA1 mutant cells. A genome-scale CRISPR-Cas9 knockout screen uncovered suppressors of the functional interaction between POLθ and BRCA1, including NBN, a component of the MRN complex, and cell-cycle regulators such as CDK6. While the MRN complex nucleolytically processes ssDNA gaps, CDK6 promotes cell-cycle progression, thereby exacerbating replication stress, a feature of BRCA1-deficient cells that lack POLθ activity. Thus, ssDNA gap formation, modulated by cell-cycle regulators and MRN complex activity, underlies the synthetic lethality between POLθ and BRCA1, an important insight for clinical trials with POLθ inhibitors.
Rights & permissions
Open Access This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons CC-BY license, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.