Niello M, Cintulová D, Raithmayr P, Holy M, Jäntsch K, Colas C, Ecker GF, Sitte HH and Mihovilovic MD (2021)
Effects of Hydroxylated Mephedrone Metabolites on Monoamine Transporter Activity in vitro
Front. Pharmacol. 12:654061.
DOI
https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2021.654061
Abstract
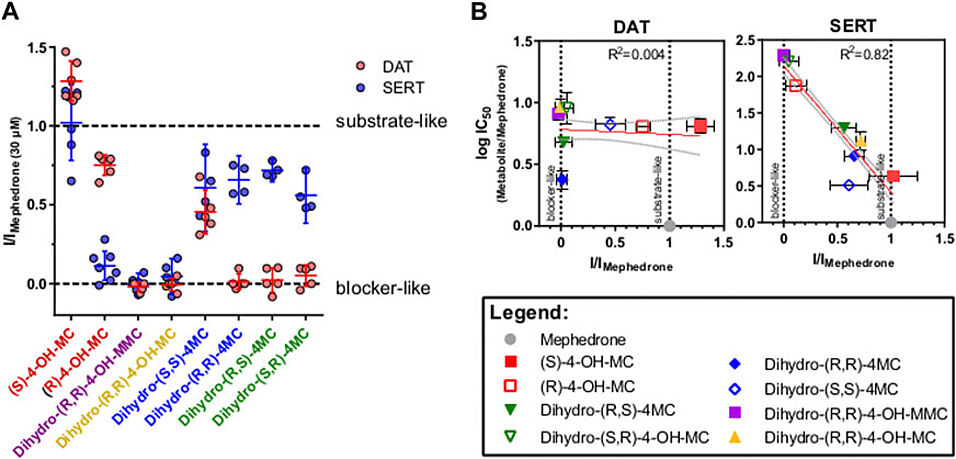
Mephedrone is a largely abused psychostimulant. It elicits the release of monoamines via the high affinity transporters for dopamine (DAT), norepinephrine (NET) and serotonin (SERT). Stereoselective metabolic reactions are involved in the inactivation and the elimination of its chemical structure. However, during these processes, several structures are generated and some of them have been reported to be still pharmacologically active. In this study 1) we have newly synthetized several putative mephedrone metabolites, 2) compared their activity at monoamine transporters, 3) generated quantitative structure activity relationships, and 4) exploited the chemical structure of the putative metabolites to screen a urine sample from a drug user and dissect mephedrone metabolism. We have found that most of the tested metabolites are weak inhibitors of monoamine transporters and that all of them are more potent at DAT and NET in comparison to SERT. The only exception is represented by the COOH-metabolite which shows no pharmacological activity at all three monoamine transporters. The enantioselectivity of mephedrone and its metabolites is present mainly at SERT, with only minor effects at DAT and NET being introduced when the β-keto group is reduced to an OH-group. Importantly, while at DAT the putative metabolites did not show changes in inhibitory potencies, but rather changes in their substrate/blocker profile, at SERT they showed mainly changes in inhibitory potencies. Molecular modeling suggests that the hydrophobic nature of a specific SERT subpocket may be involved in such loss of affinity. Finally, the assessment of the putative metabolites in one urine sample of mephedrone user displayed two previously uncharacterized metabolites, 4-COOH-nor-mephedrone (4-COOH-MC) and dihydro-4- nor-mephedrone (dihydro-4-MC). These results confirm and expand previous studies highlighting the importance of the stereochemistry in the pharmacodynamics of phase-1 metabolites of mephedrone, established their structure-activity relationships at DAT, NET and SERT and pave the way for a systematic dissection of mephedrone metabolic routes. Given the number of structures found having residual and modified pharmacological profiles, these findings may help in understanding the complex subjective effects of administered mephedrone. Moreover, the dissection of mephedrone metabolic routes may help in developing new therapies for treating psychostimulants acute intoxications.
Copyright
© 2021 Niello, Cintulová, Raithmayr, Holy, Jäntsch, Colas, Ecker, Sitte and Mihovilovic. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
Keywords
mephedrone, cathinones, metabolism, psychostimulants, monoamines, transporters, addiction, enantiomers